The good news is: your plants actually tell you exactly what is wrong.
You just have to learn their language.
If you know what to look for, changes in your plants’ leaves, stems, roots, etc. will tell you exactly which nutrients they are lacking, and which they have in abundance.
The following nutrient deficiency chart for cannabis will help you diagnose nutrient deficiencies in your weed plants. We go into more detail below that and also cover the signs of an excess of each nutrient in the chart.
Cannabis Nutrient Deficiency Chart
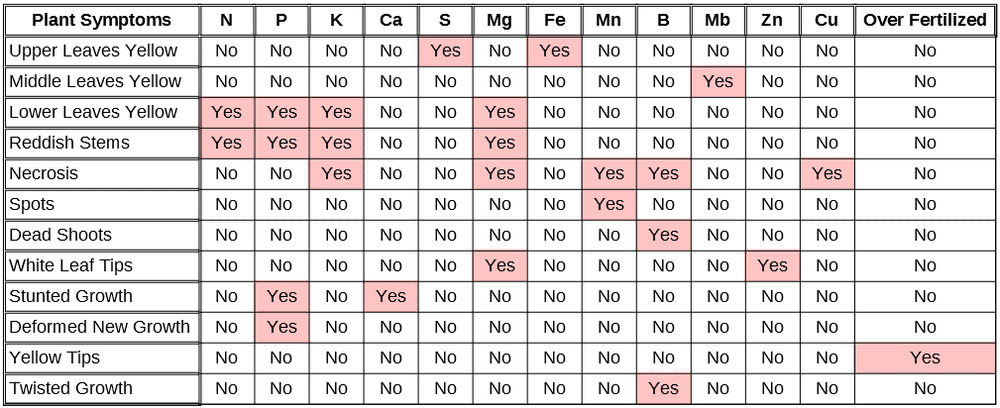
Symptoms Of Marijuana Nutrient Excesses And Deficiencies
Let’s take a more detailed look at each of the nutrients listed in the cannabis nutrient deficiency chart. We’ll examine the symptoms of both a deficiency and an excess of each one to help you ensure you know exactly how much and how often to give your weed plants nutrients.
N — Nitrogen
Deficiency
Early signs of a nitrogen deficiency are red stems and a yellowing of the lower leaves. If it continues, leaves further up the plant turn yellow, too. Eventually, you will see the marijuana leaves curling up and then droop. Plants will grow shorter and have smaller leaves. They will flower too early and produce low yields.
Excess
Too much nitrogen results in leaves turning dark great, starting from the bottom of the plant. The leaves and the stems become weak, water does not flow through the plant as it should and the harvest ends up tasting grassy.
P — Phosphorus
Deficiency
The first indication of a phosphorus deficiency is the leaves turning bluish green. The petioles will also turn purplish and overall growth slows down.
Dark blotches form on the lower leaves (copper-colored to black) and eventually, the leaves curl up, wither and die. The plant is left weak and susceptible to pests and diseases. In other words, you need to fix a phosphorus deficiency as soon as possible.
Excess
An excess of phosphorus results in newer leaves developing thin blades and interveinal chlorosis. The leaf tips and edges can burn. The plant has less internodal space and the tips of the roots begin to die. This all results in deficiencies in other nutrients (Zn, FE, Ca, Mg) and dried buds with a slight chemical taste.
K — Potassium
Deficiency
With a potassium deficiency in weed plants, older leaves turn pale and suffer chlorosis, and the edges start to develop burn. Stems become weaker and branch more often. The plant develops fewer and smaller flowers.
Excess
When a plant gets too much potassium, the symptoms are virtually identical to an excess of phosphorus. In addition to all those issues, the root zone also suffers a pH drop (it becomes more acidic).
Ca — Calcium
Deficiency
A lack of calcium causes lower leaves to curl and yellowish brown spots to form on the leaves. Flowers develop more slowly and root tips may die off. In the end, plant growth is stunted and yields suffer.
Excess
An excess of calcium cause a slight wilting of leaves also results in stunted growth. Too much calcium blocks the absorption of other nutrients, specifically iron, magnesium, manganese and potassium.
S — Sulfur
Deficiency
Plants that don’t get enough sulfur forming buds more slowly and there are fewer of them and they don’t fully grow. The first symptoms are young leaves turning light green to yellow and not growing to their full size. Over time, the veins turn yellow and the leaf tips begin to burn and hook downward. The stem can exhibit long purple streaks and sometimes turn woody.
Excess
Plants that get too much sulfur do not develop as well, with smaller and darker foliage. The tips and margins of the leaves can become discolored and burn.
Mg — Magnesium
Deficiency
A lack of sufficient magnesium first shows up after about 4 to 6 weeks, in the form of rust brown spots on more established leaves, along with interveinal yellowing.
Excess
Too much magnesium, on the other hand, causes stunted growth and darker foliage.
Fe — Iron
Deficiency
An iron deficiency can cause leaves to develop interveinal chlorosis from the base of the leaf. Leaves can also develop necrosis and drop. Overall growth of the plant slows down and yields are decreased.
Excess
Too much iron impairs the absorption of phosphorus and also results in leaves turning bronze, with dark brown spots.
Mn — Manganese
Deficiency
Not getting sufficient manganese results in interveinal chlorosis, with dark green in the edges surrounding it. Over time, dead spots develop on the affected leaves. They eventually turn pale and fall off. Young leaves are affected first and the problems spread to older leaves if the deficiency is not corrected.
Excess
Getting too much manganaese results in dark orange to dark brown mottling on the leaves. Again, it begins with the younger leaves and later affects older leaves as well.
B — Boron
Deficiency
A boron deficiency causes abnormal growth of stems, tips and roots. Shoots are contorted and look burned. Leaves become thick and brittle, with necrotic spots between the veins. Stems turn corky and take on a rusty color. Root tips can become swollen and discolored and stop growing.
Excess
An excess of boron causes leaf tips to yellow and then burn. If the plant continues to get too much boron, the whole leaves will turn yellow and begin to drop.
Mo — Molybdenum
Deficiency
Lack of molybdenum causes more established leaves to yellow and sometimes develop interveinal chlorosis. They become misshapen and the edges dry. Eventually, leaves at the bottom, and then the top, of the plant drop.
Excess
Too much molybdenum results in discolored leaves and an iron deficiency.
Zn — Zinc
Deficiency
When cannabis plants do not get enough zinc, their new leaves show interveinal chlorosis and get thin blades that are misshapen and wrinkled. Tips on the stems do not grow correctly and shoots become bunched up as a result. The tips of the leaves are discolored and burn. The leaf edges soon follow. Internodal spacing is reduced, which impacts growth and yields, which can suffer a lot.
Excess
Too much zinc rarely occurs, but if it does, you’re in trouble. Plants will quickly die from a zinc overload. Zinc blocks the ability of iron to perform its duties, which leads to a deficiency in that nutrient as well.
Cu — Copper
Deficiency
Insufficient copper causes younger leaves and shoots to wilt and die. Tips and edges of more established leaves turn dark green to copper-gray and can also die. The end result is a decreased growth rate and decreased yields.
Excess
An abundance of copper causes interveinal chlorosis and decreased branch growth. Roots also begin to either thicken and grow slower, or to decay.
Marijuana Nutrient Deficiency Table: Final Thoughts
We hope this nutrient deficiency and excess chart for growing cannabis has helped you diagnose what may be wrong with your plants. The most important thing to remember is not to panic if your weed plants show and symptoms of a nutrient deficiency or excess. Simply diagnose which nutrient the plant is getting too much (or not enough) of and adjust the amount you provide accordingly.
What is a good nutrient combo you can buy? Also, how long should I leave the grow lights on, and last but not least, is miracle grow a good product to use?
Very helpful, thanks
I’m growing in Coco with auto pots. I have a 12.4 gallon reservoir with pH water at 6.2.I am using canna nutes for coco.. my leaves are turning yellow with brown spots. How often should I water with nutrients.